Symptoms
Each patient is a unique human being.
The presentation of musician’s dystonia is extremely diverse. Each patient’s affected area is different and varies from different degrees. The presentation will also change with the type of instrument. However, under the diverse appearance, they still have something in common. The following are classified according to different body parts with four common types and symptoms.


Hand Dystonia
Among musician’s dystonias, hand dystonia is the most common. Compared with the use of daily life, musicians’ hand movements are much more complicated and refined. In addition, these movements are usually developed from an early age, so once the movement changes, even if the angle is tiny, the movement begins to stuck.
Common Symptoms of Hand Dystonia:
✔ Fingers are twisted, difficult to lift or curled inward
✔ The movement deviates from the usual track, causing more wrong notes
✔ Stiff or difficult to move, slow response
✔ Lack of control (speed, accuracy, strength)
✔ Playing inefficiently due to abnormal movements
✔ Tremors in the arm or finger/s
Embouchure Dystonia
The most prominent feature of embouchure dystonia is that it is difficult to maintain the mouth shape while playing. Due to difficulty in controlling the muscles of embouchure, making a normal sound is a challenge. In fact, there are many factors that affect embouchure dystonia. In addition to the lips, it also includes muscle control of the face, jaw, airflow and tongue. No matter which part of the problem occurs, it will affect the control of the sound.
Common Symptoms of Embouchure Dystonia:
✔ Unable to maintain embouchure and mouth corner downward
✔ It is easy to leak air in the corner of the mouth while playing
✔ Difficulties in playing a specific range
✔ Tremors in facial muscles, lips or jaws
✔ Abnormal air flow control
✔ Can’t find the proper position of the tongue
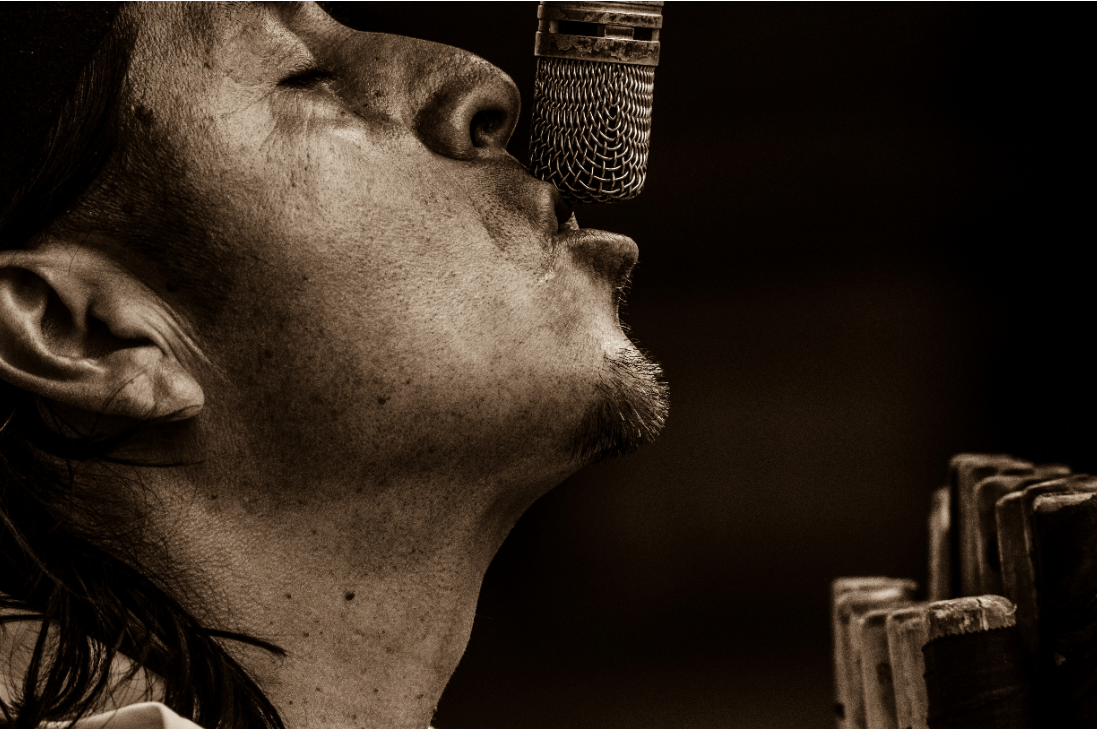

Spasmodic Dysphonia
Spasmodic dysphonia is a neurological voice disorder. The muscles that control the vocal cords spasm involuntarily, leading to interruption of sound and changes in sound quality or range. There are three types of spasmodic dysphonia: Adductor spasmodic dysphonia, Abductor spasmodic dysphonia and Mixed spasmodic dysphonia. The first type is the most common form of spasmodic dysphonia. In addition to the vocal cords, muscles control of the diaphragm, lips, and tongue may all be affected.
Common Symptoms of Spasmodic Dysphonia:
✔ Voice break, tight or breathy
✔ Intermittent sound
✔ Difficult to control the amplitude of vibrato
✔ Difficulties in singing a specific range
✔ Tremors in facial muscles, lips or jaws
✔ Abnormal air flow control
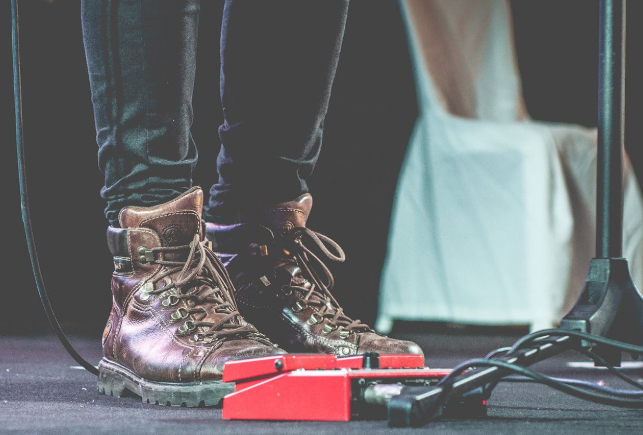
Foot Dystonia
Among musician’s dystonia, the incidence of foot dystonia is low. This is because only a small number of musical instruments are used to execute complex foot movements. Commonly affected groups are drummers or other instrument players with pedals. In fact, the range of foot dystonia includes the entire lower extremity, from the hips, legs, knees, ankles and toes. As long as any parts of them are affected, it may affect the movements of the performance.
Common Symptoms of Foot Dystonia:
✔ Unable to maintain the heel lift up
✔ Difficulty maintaining dorsiflexion in the ankle
✔ Flip the ankle to the inside
✔ The foot can’t flatten against the ground
✔ Abnormal stiffness of lower limbs
✔ The hamstring muscles are very tight

